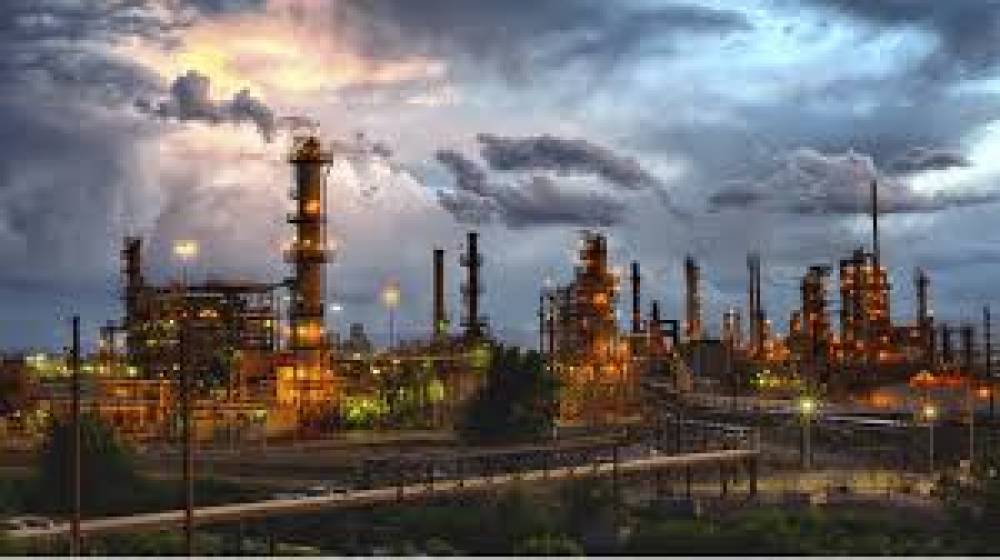

Unveiling Fugitive Emissions: Understanding the Hidden Environmental Impact
In the global fight against climate change, there is a pressing need to address all sources of greenhouse gas emissions, including a lesser-known contributor called "fugitive emissions." In this blog, we will explore the concept of fugitive emissions, shed light on its environmental impact, and discuss potential strategies to mitigate this hidden threat.
What are Fugitive Emissions?
Fugitive emissions refer to the unintended release of gases, vapors, or particles from industrial processes, transportation, and other activities. These emissions occur due to leaks, inefficient operations, or inadequate maintenance of equipment and infrastructure. Common substances associated with fugitive emissions include methane, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and various air pollutants.
The Environmental Impact of Fugitive Emissions:
Fugitive emissions contribute significantly to environmental degradation and climate change. Here are some key impacts to consider:
Climate Change: Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is a primary component of fugitive emissions. It has a higher warming potential than carbon dioxide, making it a critical driver of climate change. Fugitive methane emissions from industries, oil and gas operations, landfills, and coal mines contribute to the overall increase in global greenhouse gas concentrations.
Air Quality: Fugitive emissions release a range of air pollutants, including VOCs, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter, which are harmful to human health and ecosystems. These pollutants can lead to respiratory problems, smog formation, and the degradation of air quality in local communities.
Environmental Contamination: Leaks and spills associated with fugitive emissions can contaminate soil, water bodies, and groundwater. This contamination can have detrimental effects on ecosystems, wildlife, and the overall ecological balance.
Identifying Sources of Fugitive Emissions:
To effectively address fugitive emissions, it is essential to identify their sources. Here are some common areas where fugitive emissions occur:
Energy and Industrial Sector: Oil and gas operations, refineries, chemical plants, storage facilities, and power generation facilities are significant sources of fugitive emissions.
Transportation: Leakage from vehicles, particularly in the transportation of hazardous materials, contributes to fugitive emissions.
Waste Management: Landfills and wastewater treatment plants release methane and other greenhouse gases as organic waste decomposes.
Strategies to Mitigate Fugitive Emissions:
To curb the impact of fugitive emissions, proactive measures and innovative solutions are required. Here are some strategies to consider:
Monitoring and Detection: Implement rigorous monitoring programs to identify and promptly address fugitive emissions. Utilize advanced technologies, such as leak detection systems and drones, to improve detection efficiency.
Maintenance and Repair: Regular maintenance, inspection, and repair of industrial equipment, pipelines, and storage facilities can minimize fugitive emissions caused by leaks or equipment malfunctions.
Best Practices and Standards: Encourage the adoption of best practices and industry standards that prioritize emissions reduction and pollution prevention. Collaborate with regulatory bodies to establish stringent guidelines and regulations for fugitive emissions.
Alternative Technologies: Explore and invest in low-emission technologies, renewable energy sources, and cleaner production processes as alternatives to high-emission activities.
Public Awareness and Education: Raise awareness among industries, communities, and individuals about the environmental impact of fugitive emissions. Encourage sustainable practices, such as energy conservation, waste reduction, and responsible transportation choices.
Conclusion:
Addressing fugitive emissions is crucial for mitigating climate change, improving air quality, and safeguarding ecosystems. By recognizing the sources, understanding the impacts, and implementing effective strategies, we can make significant progress in reducing fugitive emissions. Collaboration between industries, governments, and communities is essential to drive positive change and create a sustainable


